Redshift
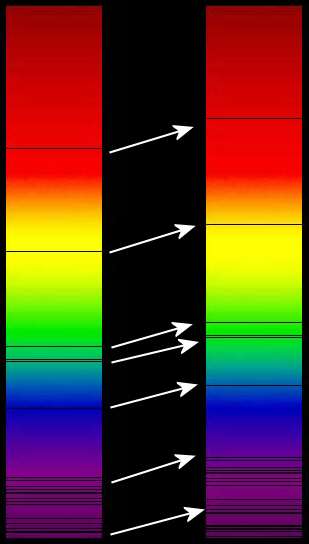
In physics and astronomy, redshift occurs when the electromagnetic radiation, usually visible light, that is emitted from or reflected off of an object is shifted towards the red end of the electromagnetic spectrum. More generally, redshift is defined as an increase in the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation] received by a detector compared with the wavelength … Read more