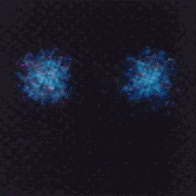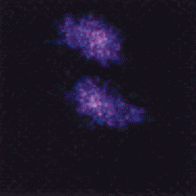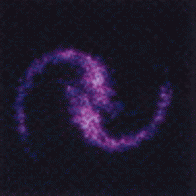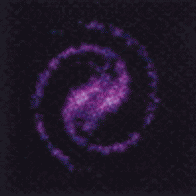
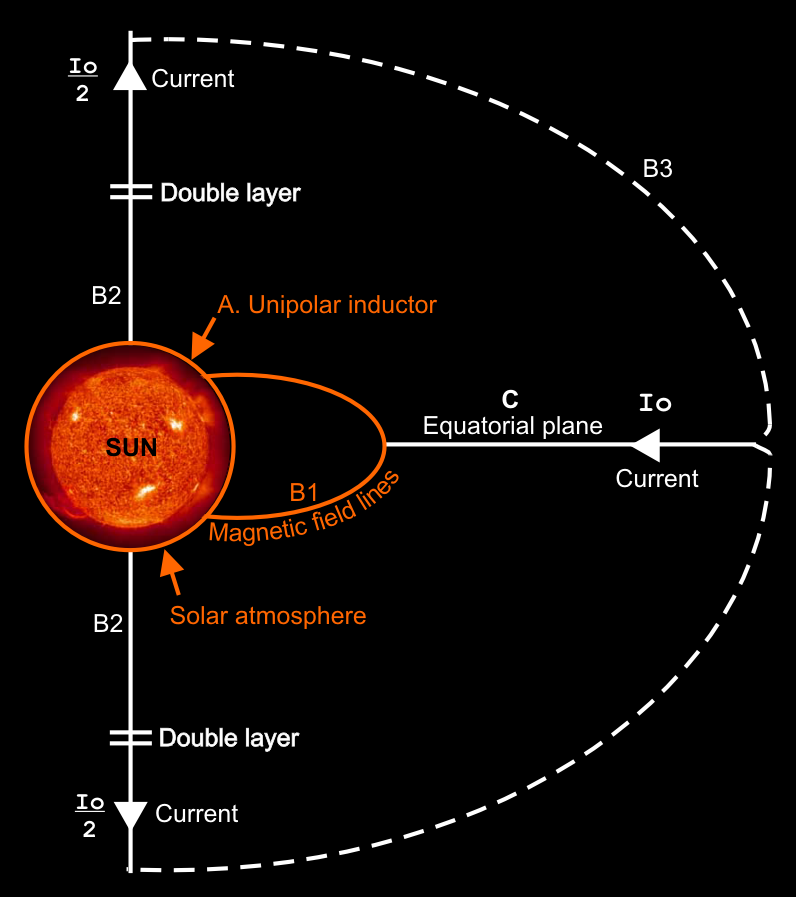
Filamentation
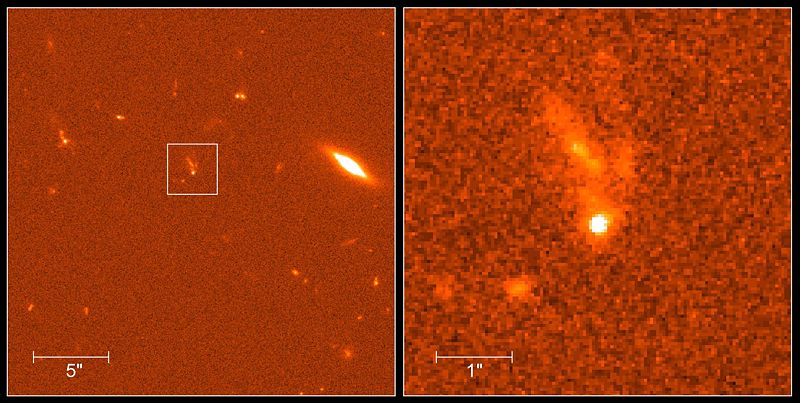
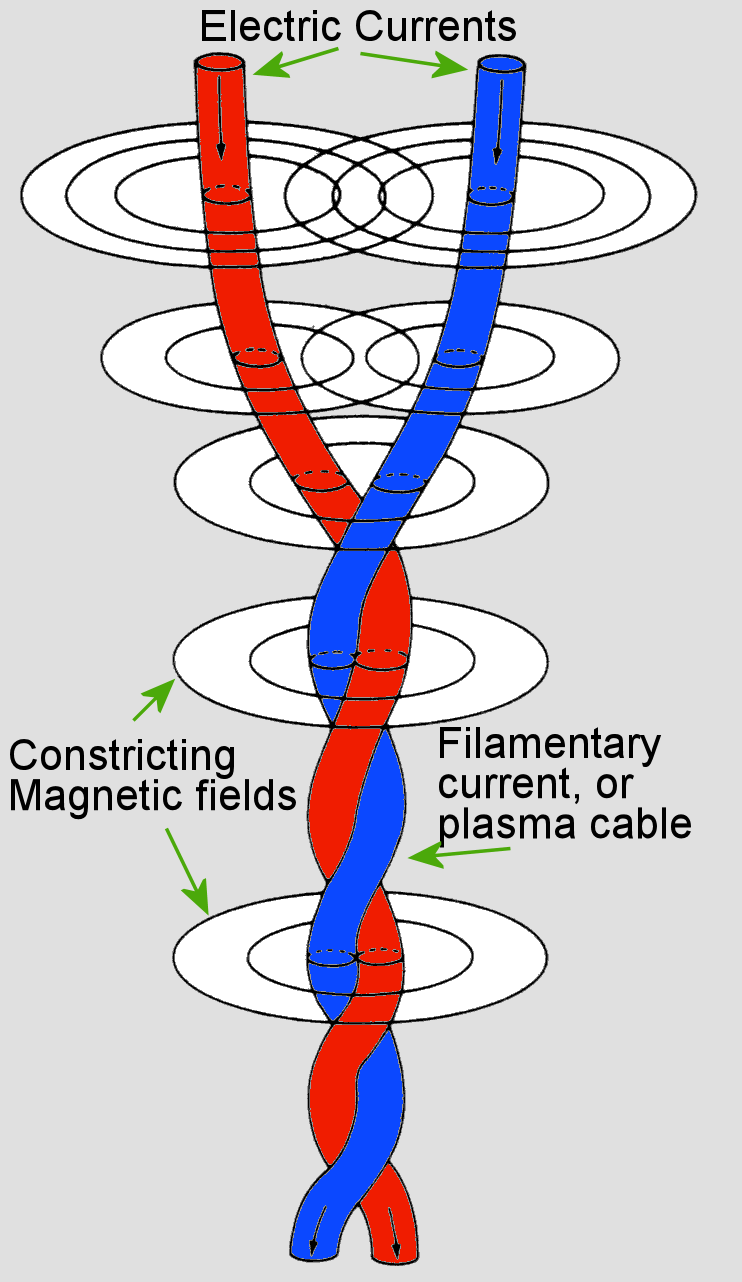
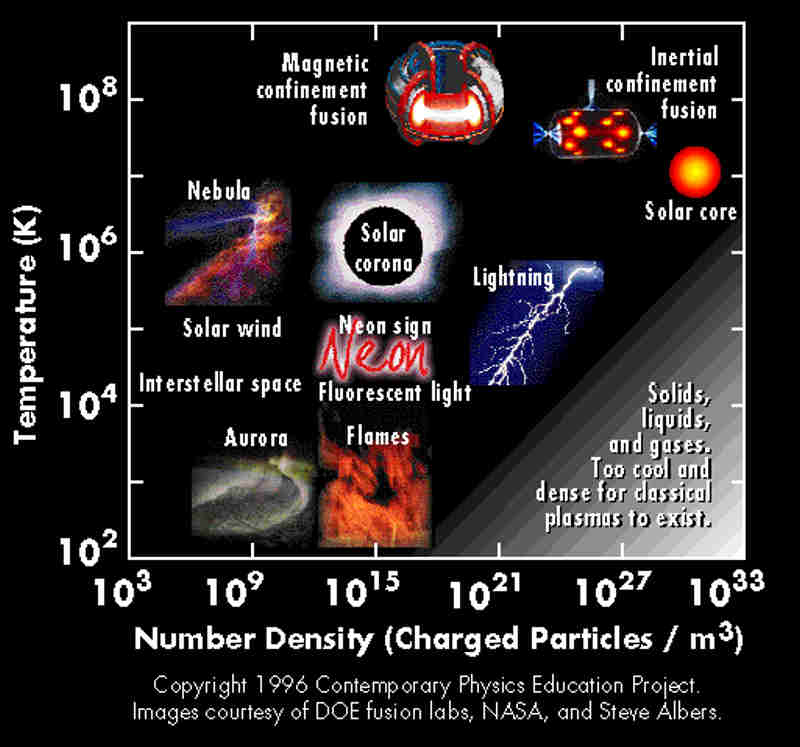
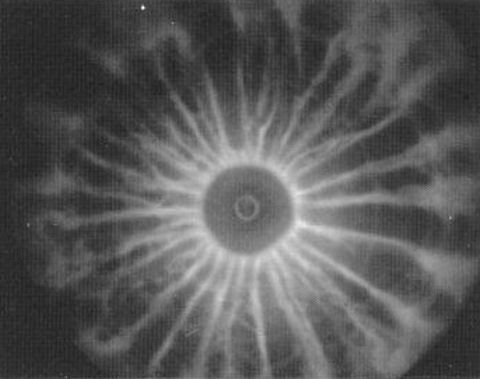
Filamentation (or filamentary structure) is often seen in plasmas. It is created because plasma contains free electrons, making it highly electrically conductive — even more than metals, and even in tenuous cosmic plasmas. As charged particles readily move in a plasma, a ring of magnetic field forms around the current that can pinch it into … Read more